Introduction
Special Tests and Procedure in Dermatology
Dermatoscopy
It is performed with a handheld instrument called a dermatoscope, providing magnification. The procedure allows for the visualization of subsurface skin structures in the epidermis, at the dermoepidermal junction, and in the papillary dermis. It improves the diagnostic accuracy of hyperpigmented lesions, as well as an early diagnosis of potentially malignant lesions.
Diascopy
This is the application of pressure to a lesión with a glass slide.- Blanching: Dilated capillaries (erythema).
- Nonblanching: Extravasated blood (purpura).
- Apple jelly sign (yellowish-brown appearance): Granulomas (sarcoidosis, necrobiosis lipoidica, skin tuberculosis and granuloma annulare).
Immunoflourescence
Skin specimens can be transported in either Michel's medium or by snap-freezing in liquid nitrogen.1. Direct immunoflourescence (DIF): Histological staining to identify the presence of tissue-bound autoantibodies and complement proteins. DIF helps to identify and differentiate various bullous diseases, including pemphigus, bullous pemphigoid, cicatricial pemphigoid, immunoglobulin (Ig) A pemphigus, dermatitis herpetiformis, epidermolysis bullosa acquisita, Henoch–Schönlein purpura, herpes gestationis or pemphigoid gestationis, lupus erythematosus.
2. Indirect immunoflourescence (IIF): Technique used in to detect circulating autoantibodies in patient serum. Antibody levels can be helpful to determine the clinical significance in pemphigus management and reflect the disease activity. KOH (potassium hydroxide). Test commonly performed investigation to detect the presence or absence of fungal elements. The standardized protocol for analyzing is to place a drop of 10 % KOH on a microscope slide that contains a skin scraping. When heated the KOH dissolves the interfering epithelial cells so that fungal elements are seen more easily. This helps aide in the identification of the fungus present in skin.

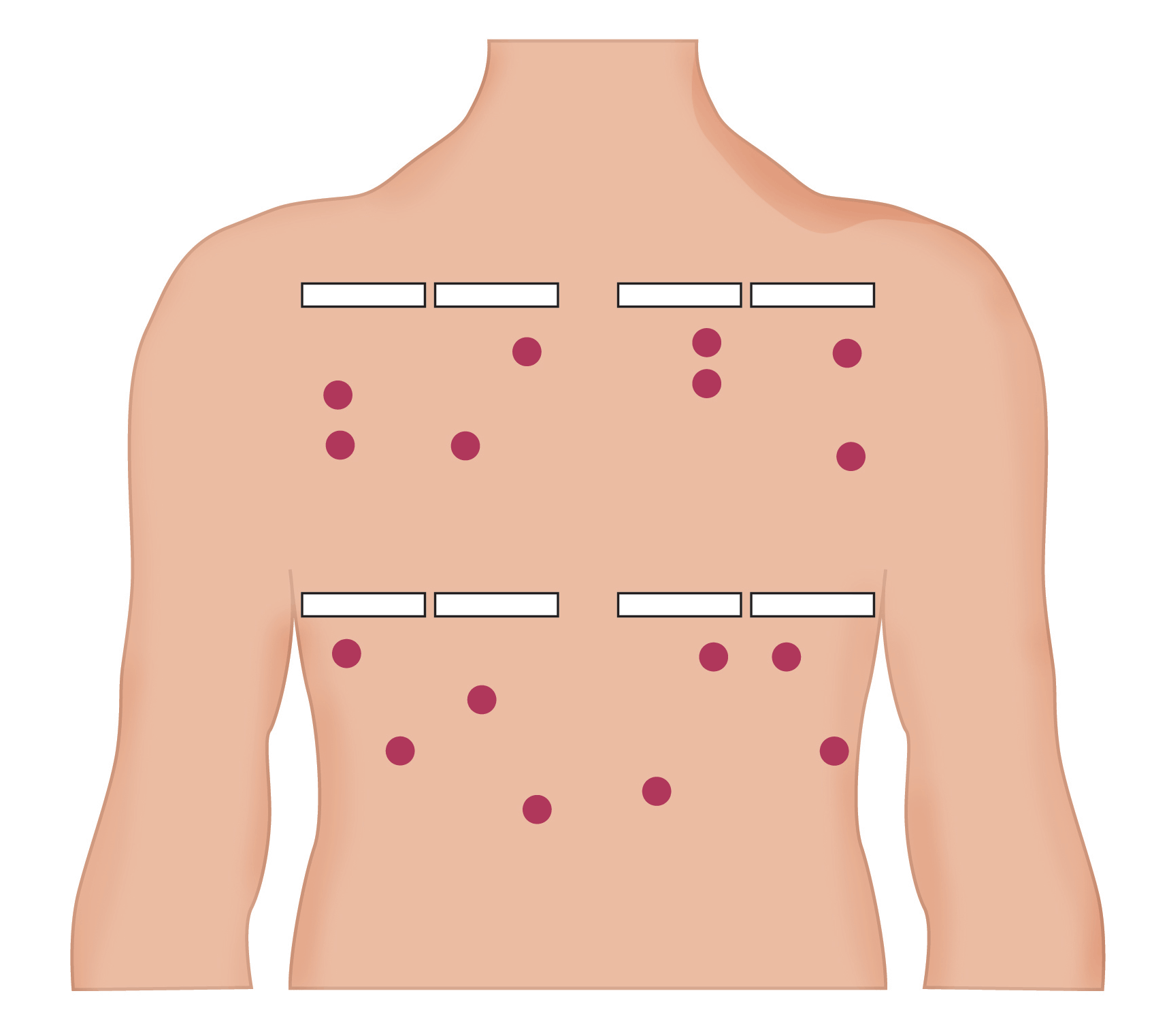
Patch test
It is a type of allergy test for contact dermatitis, a skin reaction that can develop after exposure to an allergen over several days. It can help to determine the cause of rashes, eczema or other skin irritations. During a patch test, a provider tapes patches to skin (usually, on back) that contain small amounts of potential allergens. The patches are removed after two days and check the area again another two days after removal. A delayed contact hypersensitivity reaction can manifest as papulo-vesicular reactions.Technique
A. Patches are prepared
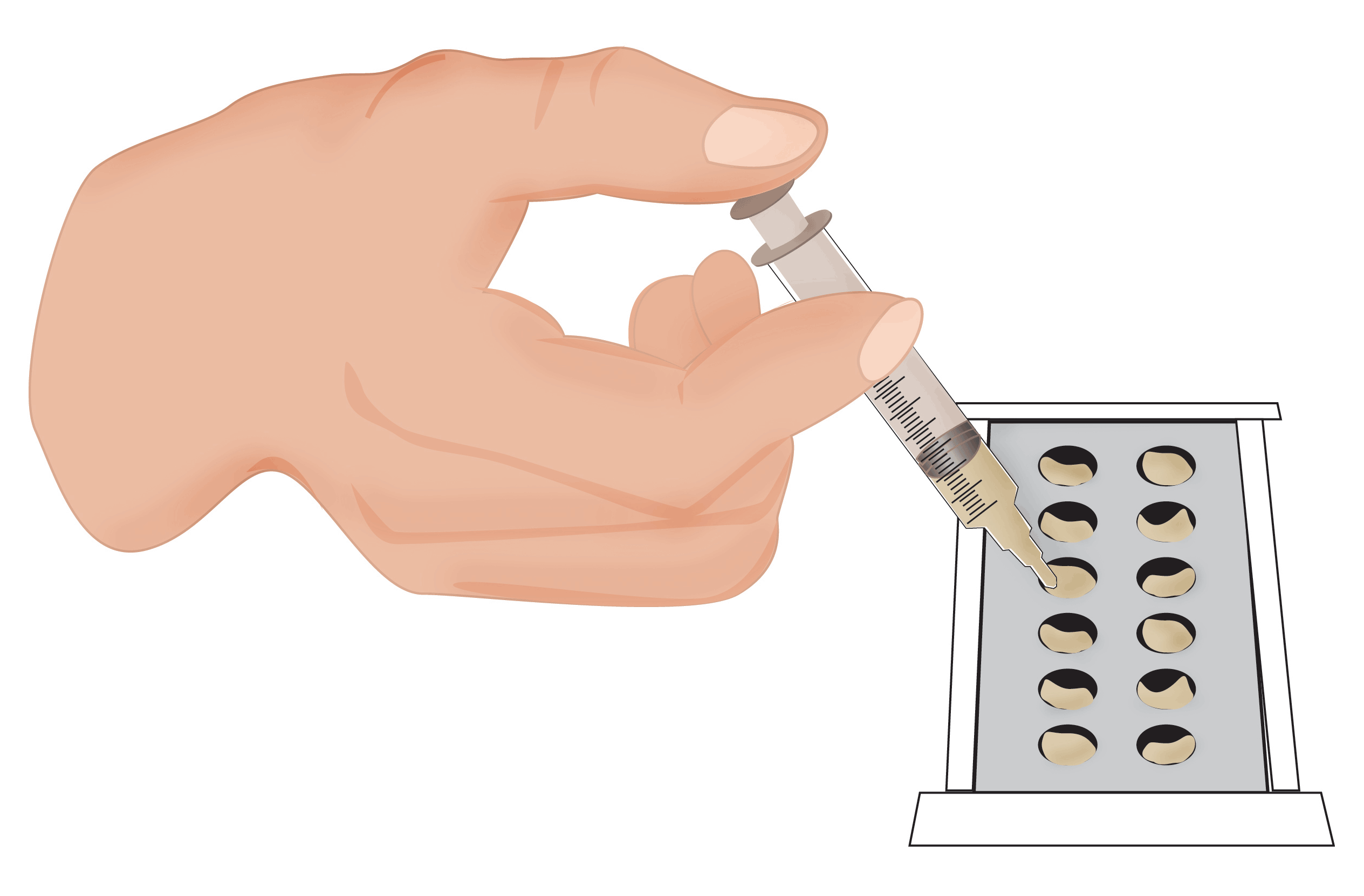 B. Patches are placed preferably on the upper back
B. Patches are placed preferably on the upper back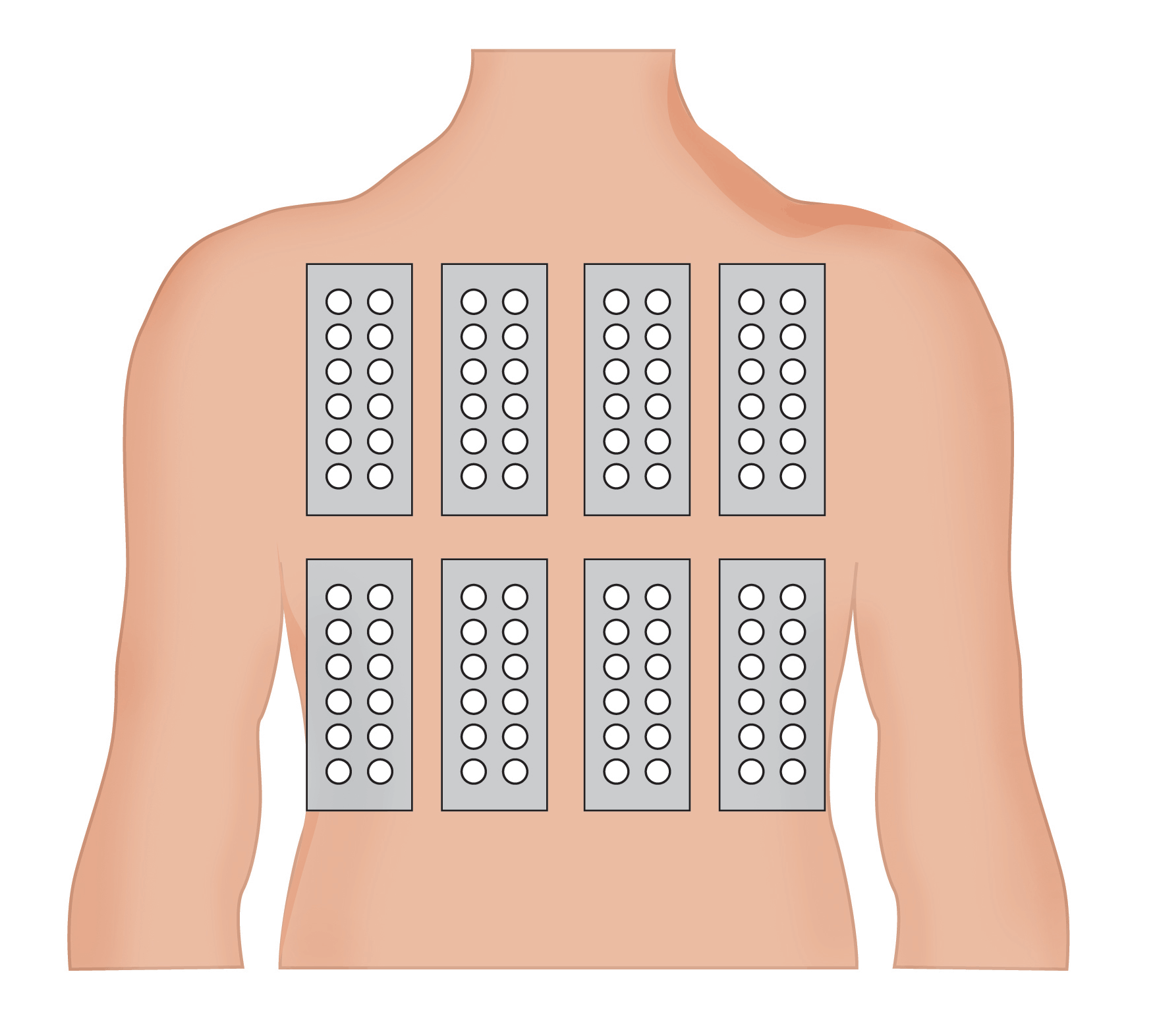 C. Hypersensitivity are determined
C. Hypersensitivity are determined